Genesis® Malleable Penile Prosthesis - Important Safety Information
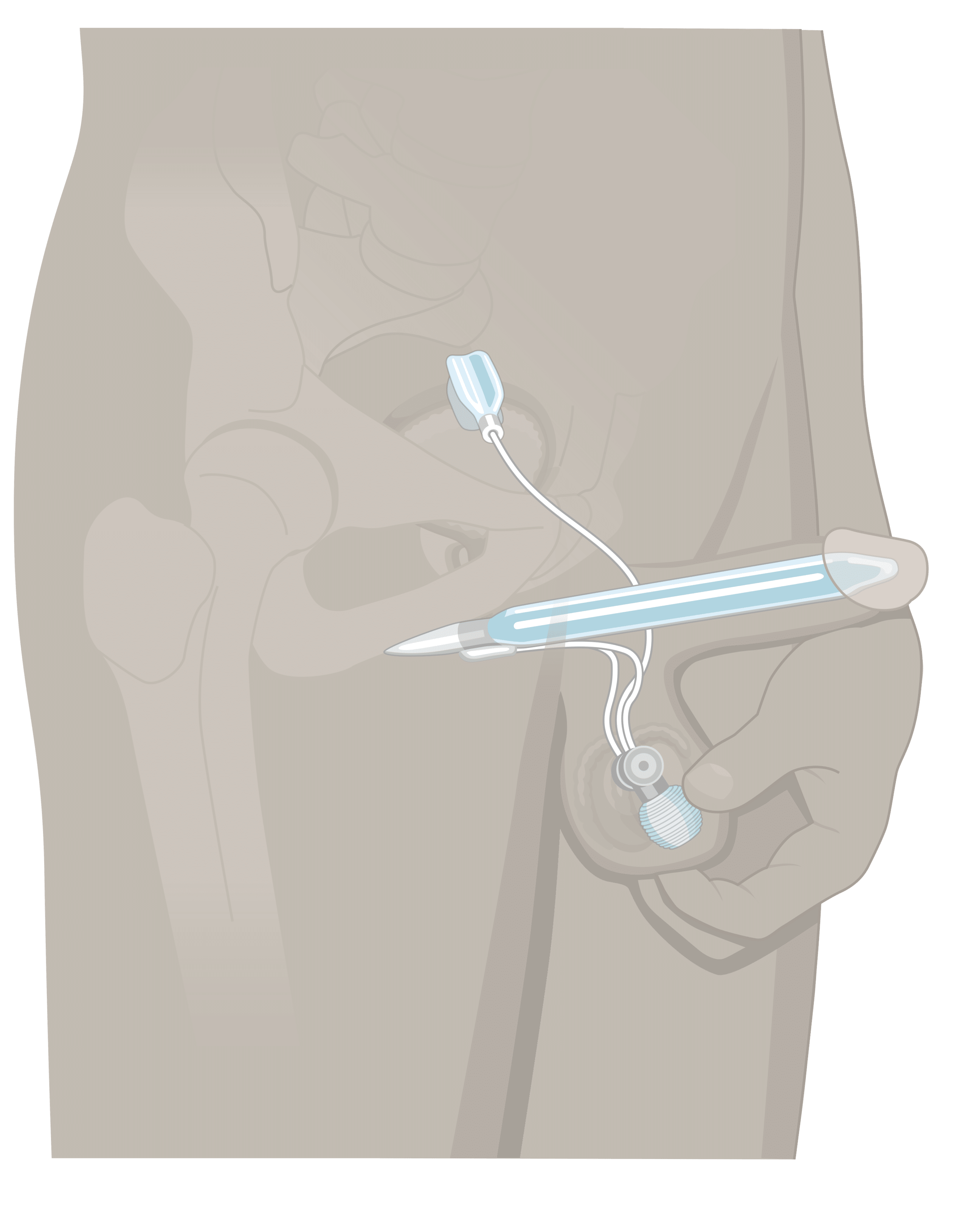
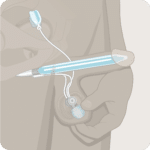
A penile implant, also called a penile prosthesis, is concealed entirely within the body to address erectile dysfunction (impotence). The device is manually positioned to simulate an erect or flaccid penis.
Intended Purpose
The Genesis Malleable Penile Prosthesis is a flexible silicone elastomer device designed to be implanted into the penis for the management of erectile dysfunction (commonly known as impotence).
Indications
The prosthesis is designed for the management of erectile dysfunction (impotence) stemming from a variety of causes, including: epispadias (a rare birth defect located at the opening of the urethra), pelvic fracture; spinal cord injury or disease; prostatectomy; cystectomy; abdominal-perineal resection (surgical removal of the anus, rectum, and sigmoid colon); multiple sclerosis; diabetes mellitus; alcoholism; arteriosclerosis and hypertensive vascular disease; priapism (prolonged and painful erection of the penis); and Peyronie’s disease (curvature of the penis). The Prosthesis may also be used in selected patients with psychogenic impotence.
Contraindications
The Genesis Malleable Penile Prosthesis should not be used in: patients with an active infection present anywhere in the body, especially urinary tract or genital infection; patients with a documented sensitivity to silicone; and, patients with unresolved urinary problems, such as an elevated residual urine volume secondary to bladder outlet obstruction or neurogenic bladder.
Warnings
Implantation of a penile Prosthesis may make natural erections difficult to achieve. It may make some other interventional treatment options not possible. Implantation of a penile Prosthesis may result in penile shortening, curvature or scarring. Men with diabetes as well as immunocompromised patients, may have an increased risk of infection which could result in permanent damage to tissue/organs.
Consult with your physician if you are experiencing a change in rigidity or appearance of the erect penis. Replacement of the prosthesis may be necessary. If you have borderline bladder decompensation, an indwelling catheter, or enlargement of the prostate talk to your doctor.
Precautions
Patients should be informed that erections achieved with a malleable penile Prosthesis may differ from original erection (e.g. not of equal length or girth) compared to what was previously experienced with natural erections. Talk with your physician regarding realistic expectations. Health conditions which hamper sexual activity (e.g. severe angina) may prevent successful use of this device. Penile implants are not considered lifetime implants due to the inherent nature of mechanical devices. Trauma to the pelvic area, such as impact injuries associated with sports, can result in damage of the implanted device and/or surrounding tissues. This damage may result in the malfunction of the device and may necessitate surgical correction, including replacement of the device.
Potential Complications
Adverse events are known to occur with penile protheses procedures and implants; some may require revision surgery or removal of the implant. Adverse events following penile protheses implantation may be new (de novo), persistent, worsening, lasting for a short time (transient), or permanent.
Penile implants are surgical solutions requiring a healing period that have risks associated with surgery such as deformity, delayed / impaired / abnormal wound healing, injury to tissue or organs (erosion / extrusion / migration) resulting in damage or loss of tissue (necrosis), opening or tunnel between tissue or organs (fistula), allergic reaction or sensitivity to device, collection of blood or fluid outside of tissue or vessels (hematoma, seroma), bleeding or excessive bleeding (hemorrhage), infection, redness or swelling of tissue, irritation, penile implant moves (migration), penile tissue dying off (necrosis), pain/discomfort, inability to pull the foreskin forward over the tip of an uncircumcised penis (paraphimosis), inability to pull the foreskin back from the tip of an uncircumcised penis (acquired phimosis), perforation or injury of soft tissue (e.g., muscles, nerves, vessels), penile structures, or organs (e.g., urethra), scarring, difficulty during sexual activity, numbness or decreased sensation in penis, blockage or slowing of urine (urethral obstruction / occlusion), urinary tract infection, and difficulty emptying bladder.
The occurrence of these events may require one or more subsequent surgeries which may or may not always fully correct the complication.
This treatment is prescribed by your physician. Discuss the treatment options with your physician to understand the risks and benefits of the various options to determine if a penile implant is right for you.
Caution: Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.